Web scraping, the process of extracting data from websites, is an invaluable tool for gathering and
analyzing information. Despite its numerous benefits, several myths and misconceptions cloud the
understanding of web scraping. These web scraping myths can often mislead both individuals and
organizations. This article is dedicated to debunking web scraping myths by addressing eight
prevalent misconceptions about the practice.
We will explore common myths related to the legality, ethics, and effectiveness of web scraping,
clarifying what is fact versus fiction. By focusing on common web scraping misconceptions, we aim
to provide a clearer perspective on how web scraping operates and its real-world applications.
Understanding the web scraping truths is crucial for making informed decisions about utilizing this
tool effectively. This article will highlight how web scraping accuracy can be maintained and the best
practices to ensure ethical and legal compliance. By dispelling these myths, we hope to shed light on
the true potential of web scraping and its role in modern data analysis and business intelligence.
Myth 1: Web Scraping is Illegal
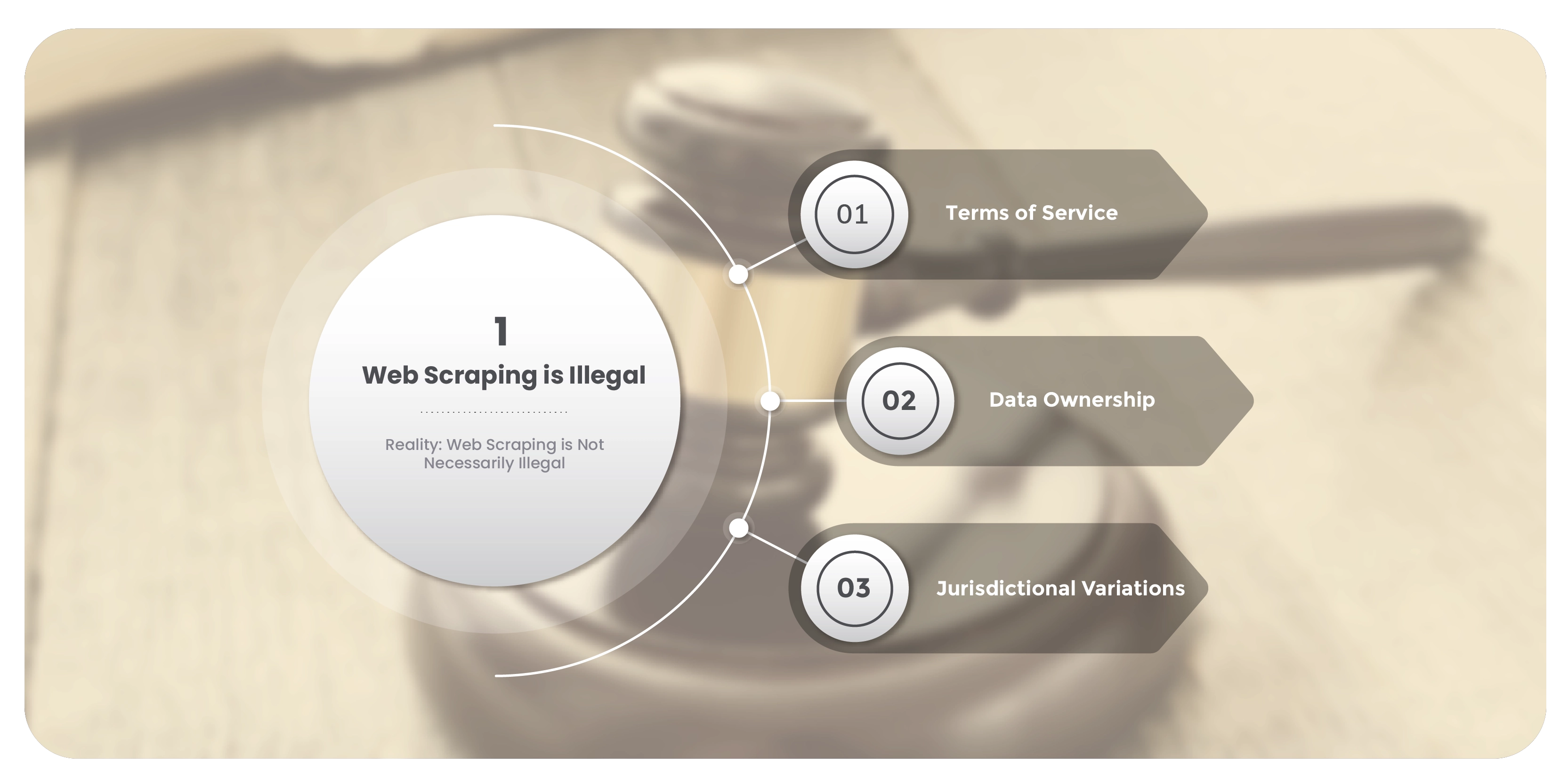
Reality: Web Scraping is Not Necessarily Illegal
One of the most pervasive myths is that web scraping is inherently illegal. The legality of web
scraping lies on multiple factors, including the jurisdiction, the website's terms of service, and the
nature of the data being scraped. Understanding web scraping facts vs. fiction is crucial to
navigating these complexities.
Terms of Service: Many websites possess terms of service that openly prohibit scraping. Violating
these terms can result in legal action. However, not all websites impose such restrictions, and
scraping public data not protected by copyright or proprietary rights often falls within legal
boundaries. This highlights the importance of considering web scraping legal issues in each case.
Data Ownership: Scraping public data that does not involve unauthorized access or breach of
proprietary databases is generally legal. For instance, scraping data from publicly available product
listings on e-commerce sites is usually permissible, provided it adheres to web scraping ethics.
Jurisdictional Variations: Laws to Scrape eCommerce Product Data can vary significantly by country. For example, in the United States, scraping public data may be permissible under certain conditions, while strict data protection regulations might apply in other countries. Understanding these regional differences is vital for ensuring compliance.
Myth 2: Web Scraping Violates Privacy Laws
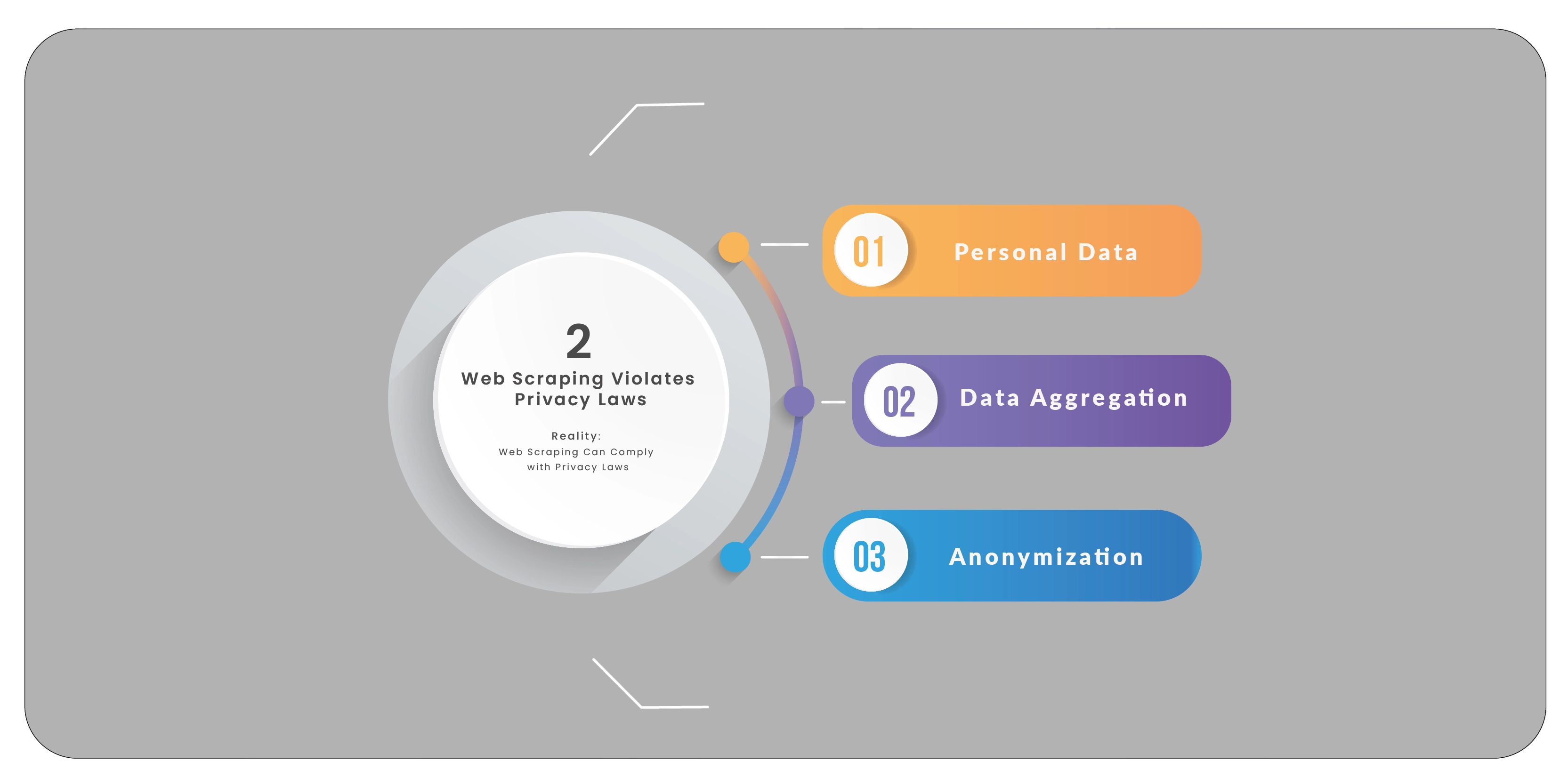
Reality: Web Scraping Can Comply with Privacy Laws
Another common myth is that web scraping automatically violates privacy laws. While privacy laws
are essential for protecting personal information, web scraping does not inherently breach these
laws when conducted responsibly. Addressing web scraper misconceptions is critical to
understanding this issue.
Personal Data: Scraping personal data, such as email addresses or phone numbers, without
consent can indeed violate privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the
European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. It is crucial to avoid
scraping sensitive personal data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. This
highlights web scraping challenges related to privacy.
Data Aggregation: Privacy concerns are generally less pronounced when scraping aggregated, non-
personally identifiable information. For instance, extracting product prices and reviews from an e-
commerce site without personal user data usually complies with privacy laws. This aligns with web
scraping facts, which is about responsible data collection.
Anonymization: If personal data is anonymized during the scraping process, the risk of privacy
violations is minimized. Ensuring that data cannot be traced back to individual users helps comply
with privacy regulations, mitigating web scraping challenges and ensuring adherence to privacy
standards.
Myth 3: Web Scraping is the Same as Data Mining

Reality: Web Scraping and Data Mining are Different
Web scraping and data mining are often conflated, but they are distinct processes with different
objectives and methods.
Web Scraping: Web Scraping Retail Websites Data is useful when APIs are unavailable or do not provide the required data. It allows for extracting information directly from web pages, including content that may not be accessible through APIs.
Data Mining: Data mining, on the other hand, involves analyzing large datasets to identify
patterns, correlations, and insights. It typically occurs after collecting data and involves
complex statistical and computational techniques.
Complementary Tools: While web scraping gathers raw data, data mining analyzes and
derives actionable insights from that data. Both processes are complementary but serve
different purposes in data analysis.
Myth 4: Web Scraping is a Viable Solution for All Data Collection Needs

Reality: Web Scraping Has Limitations
While web scraping is a powerful tool, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution for data collection. Several
limitations and challenges should be considered:
Dynamic Content: Websites that use JavaScript to load content dynamically can be challenging for
web scraping. Scraping tools may struggle to access content not directly available in the HTML
source. This is a crucial aspect of web scraping service misunderstandings.
Anti-Scraping Measures: Many websites implement anti-scraping measures, such as CAPTCHA, IP
blocking, and rate limiting. These measures can hinder scraping efforts and require sophisticated
techniques to bypass. Understanding these limitations helps address myths about web scraping
tools.
Data Accuracy: The accuracy of scraped data can vary depending on the website's structure and
the quality of the scraping tool. Regular maintenance and updates to scraping scripts may be needed
to ensure data accuracy. Professional web scraping services often provide solutions to maintain high
data quality.
Legal and Ethical Constraints: Certain types of data or websites may have legal and ethical
restrictions that make scraping impractical or inadvisable. Consider these factors when planning a
scraping project to navigate potential web scraping service misunderstandings.
Myth 5: Web Scraping is Expensive and Complex
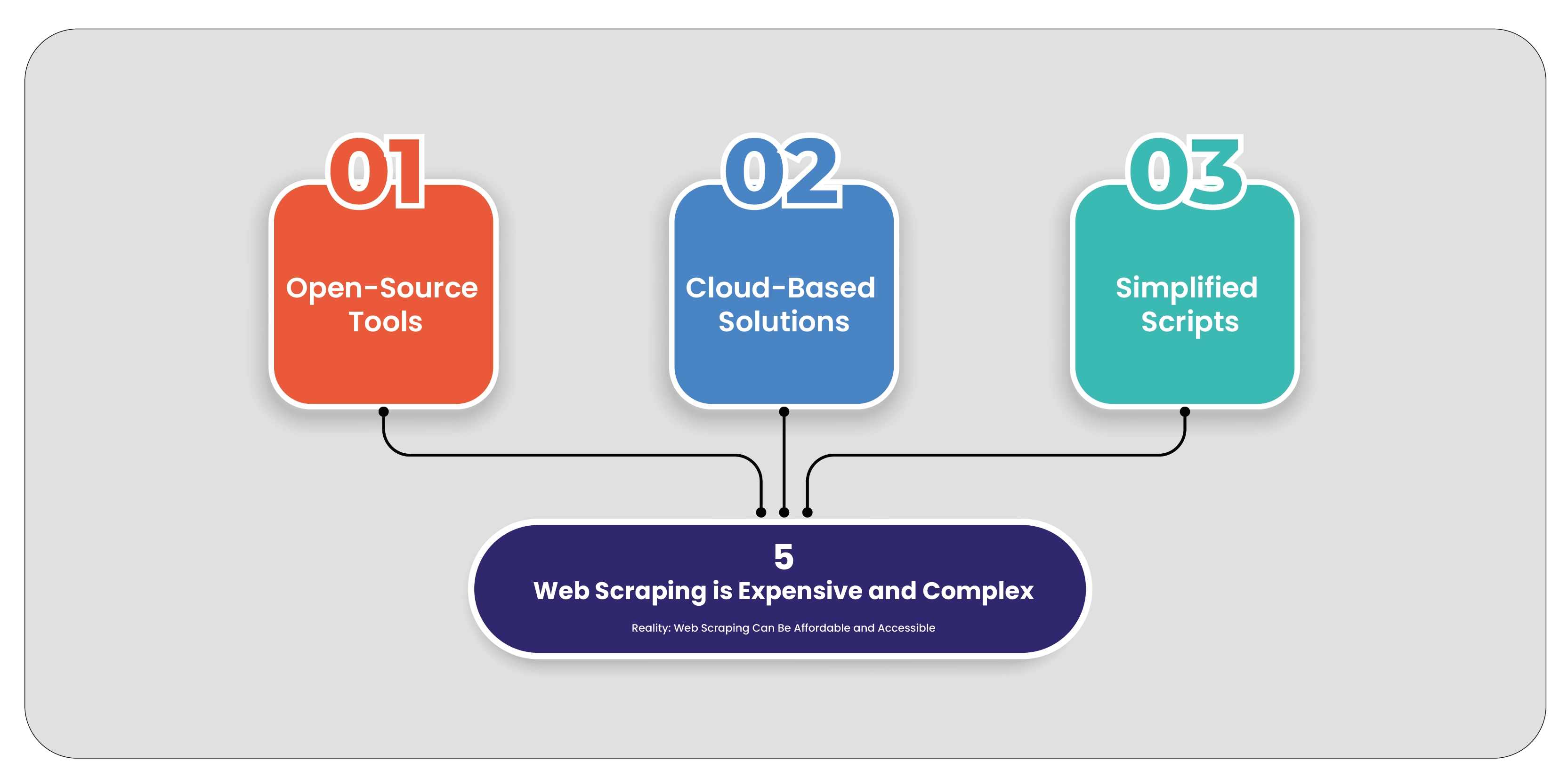
Reality: Web Scraping Can Be Affordable and Accessible
The belief that web scraping is prohibitively expensive and complex is a misconception. Advances in
technology have made web scraping more accessible and cost-effective.
Open-Source Tools: Numerous open-source web scraping tools and libraries, such as
BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Puppeteer, are available. These tools can be used for free or at a
low cost, reducing the overall expense of web scraping.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Many cloud-based scraping services offer affordable pricing models
based on the volume of data scraped. These services handle the technical complexities,
making web scraping accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Simplified Scripts: Writing simple scraping scripts is relatively straightforward for those with
basic programming skills. Online tutorials and resources can help individuals get started with
minimal investment.
Myth 6: Web Scraping Causes Significant Server Load
Reality: Responsible Scraping Practices Minimize Server Load
The idea that web scraping inevitably causes significant server load is inaccurate. Responsible and
ethical scraping practices can minimize the impact on target websites.
Rate Limiting: Implementing rate limits and respecting website policies regarding request
frequency can help prevent overloading servers. Scraping tools can be configured to make
frequent requests that do not strain server resources.
Robots.txt: Many websites use the robots.txt file to specify crawling rules and limits.
Respecting these guidelines helps reduce server load and ensures that scraping activities are
conducted responsibly.
Polite Scraping: Adopting polite scraping practices, such as making requests during off-peak
hours and limiting the number of concurrent connections, helps minimize server impact and
maintains good relationships with website owners.
Myth 7: Web Scraping is a Black Hat Technique
Reality: Web Scraping Can Be Ethical and Legitimate
Web scraping is often associated with black hat tactics, but it can be conducted ethically and
legitimately when used for valid purposes.
Ethical Use Cases: Many businesses use web scraping for legitimate purposes, such as competitive analysis, Pricing Strategies, market research, and price monitoring. Web scraping is a valuable tool when conducted transparently and by legal and ethical guidelines.
Permission and Collaboration: In some cases, obtaining permission from website owners or
collaborating with them can enhance the legitimacy of web scraping activities. Some
websites offer APIs or data access agreements that facilitate data collection in a controlled
manner.
Transparency: Being transparent about the purpose and scope of web scraping activities
helps build trust and demonstrates ethical practices. Communicating intentions and
adhering to ethical standards can mitigate concerns about black hat tactics.
Myth 8: Web Scraping is Obsolete with the Rise of APIs
Reality: Web Scraping and APIs Serve Different Purposes
The rise of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) has led to the misconception that web
scraping is obsolete. However, web scraping and APIs serve different functions and complement
each other in data collection.
APIs: APIs provide a structured and efficient way to access data from websites and services.
They offer standardized endpoints and data formats, making integrating and using data
more accessible.
Web Scraping: Web scraping is useful when APIs are unavailable or do not provide the
required data. It allows for extracting information directly from web pages, including content
that may not be accessible through APIs.
Combination Approach: Many data-driven projects combine APIs and Liquor Data Scraping Service to gather comprehensive data. APIs are used for structured data access, while web scraping fills in gaps where APIs are lacking.
Conclusion
Ecommerce Data Collection Service is a powerful and versatile tool for data collection, but various myths and misconceptions surround it. By understanding the realities behind these myths, businesses and individuals can use web scraping more effectively and responsibly. It is essential to approach Grocery Data Scraping Service with a clear understanding of its legal, ethical, and practical aspects, ensuring that data collection activities are compliant and respectful.
Debunking these myths helps clarify web scraping's true nature and highlights its potential as a
valuable tool for accessing and analyzing online data.
At Product Data Scrape, we strongly emphasize ethical practices across all our services, including
Competitor Price Monitoring and Mobile App Data Scraping. Our commitment to transparency and integrity is at the heart of everything we do. With a global presence and a focus on personalized
solutions, we aim to exceed client expectations and drive successs in data analytics. Our dedication
to ethical principles ensures that our operations are both responsible and effective.





































.webp)





.webp)
.webp)